Are Concave Mirrors Converging Or Diverging
News Leon
Mar 15, 2025 · 6 min read
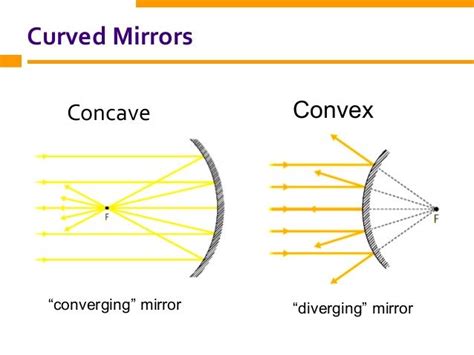
Table of Contents
Are Concave Mirrors Converging or Diverging? Understanding Mirror Types and Their Applications
The world of optics can be fascinating and sometimes confusing. Understanding the behavior of mirrors, especially concave mirrors, is crucial for anyone interested in physics, photography, astronomy, or even everyday applications like makeup mirrors. One of the fundamental questions that often arises is: are concave mirrors converging or diverging? The answer, simply put, is converging. However, understanding why this is the case requires a deeper dive into the properties of concave mirrors and how they interact with light. This comprehensive guide will explore this topic thoroughly, covering the characteristics of concave mirrors, their applications, and how they differ from their convex counterparts.
Understanding Reflection and Mirrors
Before we delve into the specifics of concave mirrors, let's establish a basic understanding of reflection. Reflection is the bouncing back of light rays when they strike a surface. The angle at which the light ray strikes the surface (angle of incidence) is equal to the angle at which it reflects (angle of reflection). This principle, known as the law of reflection, governs the behavior of all mirrors.
Mirrors are classified into two main types based on their shape:
- Concave mirrors: These mirrors have a reflecting surface that curves inward, like the inside of a sphere.
- Convex mirrors: These mirrors have a reflecting surface that curves outward, like the outside of a sphere.
The curvature of the mirror's surface significantly influences how it reflects light and, consequently, whether it converges or diverges light rays.
Concave Mirrors: Converging Light Rays
A concave mirror is characterized by its inward-curving reflective surface. This curvature plays a crucial role in its converging nature. When parallel rays of light strike a concave mirror, they reflect and converge at a single point called the focal point (F) or principal focus. The distance between the focal point and the mirror's surface is called the focal length (f).
How Concave Mirrors Converge Light: A Detailed Explanation
The converging effect of a concave mirror stems from the way the light rays interact with its curved surface. Consider parallel rays of light approaching the mirror:
-
Rays near the principal axis: Rays that strike the mirror close to its principal axis (the line passing through the center of curvature and the mirror's center) reflect and pass through the focal point. This is a direct consequence of the law of reflection and the mirror's curvature. The closer the ray is to the principal axis, the more accurately it will pass through the focal point.
-
Rays further from the principal axis: Rays that strike the mirror further from the principal axis also reflect and converge, although they may not precisely intersect at the focal point. The further a ray is from the principal axis, the greater the deviation from the precise focal point. However, the overall effect is still convergence.
The converging nature of a concave mirror allows it to form real and inverted images under certain conditions. A real image is formed when the light rays actually converge at a point, and it can be projected onto a screen. In contrast, a virtual image is formed when light rays appear to diverge from a point but do not actually converge there.
Real and Virtual Images Formed by Concave Mirrors
The type of image formed by a concave mirror depends on the object's position relative to the mirror's focal point and center of curvature.
-
Object beyond the center of curvature (C): A real, inverted, and diminished image is formed between the focal point (F) and the center of curvature (C).
-
Object at the center of curvature (C): A real, inverted, and same-size image is formed at the center of curvature (C).
-
Object between the center of curvature (C) and the focal point (F): A real, inverted, and magnified image is formed beyond the center of curvature (C).
-
Object at the focal point (F): No image is formed (rays are parallel after reflection).
-
Object between the focal point (F) and the mirror: A virtual, upright, and magnified image is formed behind the mirror. This is the type of image you see in a makeup mirror.
Applications of Concave Mirrors: Leveraging the Converging Power
The converging properties of concave mirrors make them incredibly versatile and useful in various applications, including:
-
Telescopes: Large concave mirrors are used in reflecting telescopes to gather and focus light from distant celestial objects, enabling astronomers to observe stars, galaxies, and other astronomical phenomena.
-
Headlights and Searchlights: Concave mirrors are used in headlights and searchlights to concentrate light into a parallel beam, maximizing the intensity and range of the light.
-
Solar Furnaces: Concave mirrors can be used to concentrate sunlight onto a small area, generating high temperatures, which are used in solar furnaces.
-
Microscopes: Concave mirrors are used in some types of microscopes to focus light onto the specimen.
-
Satellite Dishes: These parabolic reflectors are essentially large concave mirrors that focus radio waves from satellites onto a receiver.
-
Medical Equipment: Concave mirrors are found in certain medical instruments for focusing light or imaging purposes.
-
Reflecting Ophthalmoscopes: These instruments utilize concave mirrors to illuminate and examine the interior of the eye.
Comparing Concave and Convex Mirrors: Converging vs. Diverging
In contrast to concave mirrors, convex mirrors are diverging. They always produce virtual, upright, and diminished images, regardless of the object's position. This is because the curvature of the convex mirror causes the reflected rays to spread out, or diverge. Convex mirrors are often used in applications where a wider field of view is required, such as:
-
Car side mirrors: The convex shape provides a broader view of the surroundings, improving safety.
-
Security mirrors: These are used in shops and other locations to monitor a wide area.
Understanding the Radius of Curvature and Focal Length
It's important to understand the relationship between the radius of curvature (R) and the focal length (f) of a concave mirror. The focal length is approximately half the radius of curvature: f ≈ R/2. This relationship is crucial for calculating image positions and sizes using the mirror equation and magnification formula.
The Mirror Equation and Magnification
The mirror equation and magnification formula are essential tools for analyzing the behavior of concave mirrors:
-
Mirror Equation: 1/f = 1/u + 1/v where 'f' is the focal length, 'u' is the object distance, and 'v' is the image distance.
-
Magnification (M): M = -v/u where 'v' is the image distance and 'u' is the object distance. A negative magnification indicates an inverted image.
Conclusion: Concave Mirrors – Converging Power with Versatile Applications
In conclusion, concave mirrors are indeed converging mirrors. Their inward-curving surface causes parallel light rays to converge at the focal point, enabling the formation of real and virtual images depending on the object's position. This converging property, along with the ability to manipulate image size and orientation, makes concave mirrors invaluable in a wide range of applications, from astronomical observation to everyday household items. Understanding their behavior and properties is essential for anyone seeking to grasp the principles of optics and their practical implications in various fields. The ability to calculate image characteristics using the mirror equation and magnification formula solidifies our understanding of the power and precision offered by this fundamental optical device.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Frameshift Mutation Could Result From
Mar 15, 2025
-
What Percent Of 85 Is 17
Mar 15, 2025
-
Government By One Person Is Called
Mar 15, 2025
-
Is A Diamond An Element Compound Or Mixture
Mar 15, 2025
-
A 3 2a 2 A 2
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Are Concave Mirrors Converging Or Diverging . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
