A Rod Shaped Bacterium Is Called A
News Leon
Mar 16, 2025 · 6 min read
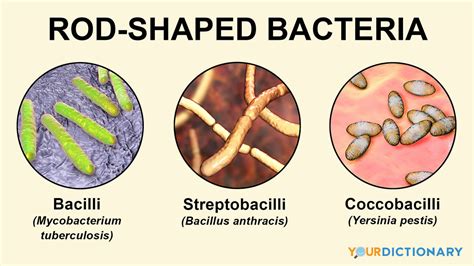
Table of Contents
A Rod-Shaped Bacterium is Called a Bacillus: A Deep Dive into Morphology, Genetics, and Significance
Rod-shaped bacteria, formally known as bacilli (singular: bacillus), represent a diverse and significant group of microorganisms impacting various aspects of our lives, from environmental processes to human health. Understanding their morphology, genetics, and ecological roles is crucial in various scientific fields, including microbiology, medicine, and biotechnology. This comprehensive article delves into the fascinating world of bacilli, exploring their characteristics, classification, and importance.
Understanding Bacterial Morphology: Beyond the Rod Shape
Before focusing specifically on bacilli, it's essential to grasp the broader context of bacterial morphology. Bacteria exhibit a remarkable array of shapes and sizes, which contribute significantly to their identification and classification. While rod shape is a defining feature of bacilli, variations exist within this category. We encounter:
- Cocci: Spherical or ovoid bacteria.
- Bacilli: Rod-shaped bacteria.
- Spirilla: Spiral-shaped bacteria.
- Vibrio: Comma-shaped bacteria.
The morphology is influenced by the bacterial cell wall and cytoskeleton. The cell wall provides structural rigidity and shape, while the cytoskeleton plays a role in maintaining cell shape and facilitating cell division. These structural elements are influenced by genetic factors and environmental conditions, meaning that the shape of a bacterium can sometimes vary depending on its surroundings.
Variations Within Bacillus Morphology:
Even within the bacillus category, we see diversity:
- Coccobacilli: These are short, plump rods that almost appear coccus-like, blurring the lines between the two morphologies. Their identification often relies on more detailed analyses beyond simple microscopic observation.
- Fusiform bacilli: These bacilli are spindle-shaped, tapering towards their ends. This distinct shape gives them a unique appearance under the microscope.
- Filamentous bacilli: These bacilli are exceptionally long and slender, sometimes forming filaments or chains. Their elongated shape differs significantly from the typical rod shape.
These morphological variations underscore the complexity and adaptability of bacteria, highlighting the need for comprehensive identification techniques beyond simple visual observation.
The Bacillus Genus: A Diverse Group of Rod-Shaped Bacteria
While the term "bacillus" refers to the rod shape generally, the genus Bacillus represents a specific group of rod-shaped, Gram-positive bacteria. This genus stands out due to its members' ability to form endospores, highly resistant structures that allow the bacteria to survive harsh environmental conditions, such as heat, radiation, and desiccation. This endospore formation is a crucial characteristic used in their identification and classification.
Key Characteristics of Bacillus Species:
- Gram-positive: They stain purple in a Gram stain, indicating a thick peptidoglycan layer in their cell wall.
- Aerobic or facultatively anaerobic: Most species can grow in the presence or absence of oxygen, although some are strictly aerobic.
- Spore-forming: Endospore formation is a defining characteristic of many Bacillus species, offering remarkable survival capabilities.
- Ubiquitous distribution: Bacillus species are found in a wide variety of environments, including soil, water, and the air.
Notable Examples of Bacillus Species:
- Bacillus subtilis: A common soil bacterium, often used as a model organism in microbiology research due to its genetic tractability and ease of cultivation. It is also explored for biotechnological applications.
- Bacillus anthracis: The causative agent of anthrax, a serious zoonotic disease. Its ability to form highly resistant spores makes it a potential bioterrorism threat.
- Bacillus cereus: A foodborne pathogen causing food poisoning through the production of toxins. It's commonly associated with improperly cooked rice.
- Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt): A bacterium producing insecticidal toxins, widely used as a biological pesticide in agriculture. Its use is considered environmentally friendly compared to chemical pesticides.
The Genetics of Bacilli: Understanding Diversity and Evolution
The genetic makeup of bacilli is crucial in understanding their diversity, adaptability, and pathogenic potential. Their genomes vary in size and content, reflecting the range of lifestyles and ecological niches they occupy. Genetic analyses, including whole-genome sequencing, have revolutionized our understanding of bacilli, revealing insights into:
- Horizontal gene transfer: The acquisition of genetic material from other organisms contributes significantly to their genetic diversity, influencing traits such as antibiotic resistance and toxin production.
- Evolutionary relationships: Phylogenetic studies using genetic data clarify the evolutionary relationships between different Bacillus species and their placement within the broader bacterial phylogenetic tree.
- Pathogenicity mechanisms: The genetic basis for pathogenicity in Bacillus species, such as B. anthracis and B. cereus, has been extensively studied, leading to the development of diagnostic and therapeutic strategies.
- Metabolic pathways: Genome sequencing helps elucidate the metabolic pathways in various Bacillus species, identifying potential applications in biotechnology, such as enzyme production and bioremediation.
The Significance of Bacilli: Impacts Across Various Fields
Bacilli play crucial roles in various aspects of life, from environmental processes to industrial applications and human health. Their significance spans multiple fields:
1. Environmental Microbiology:
- Nutrient cycling: Many Bacillus species are involved in nutrient cycling in soil ecosystems, contributing to decomposition and the release of essential nutrients for plant growth. Their role in decomposition of organic matter is significant.
- Bioremediation: Some bacilli are capable of degrading pollutants, making them valuable tools for bioremediation efforts aimed at cleaning up contaminated environments. Their ability to break down various compounds is actively studied.
- Nitrogen fixation: Certain Bacillus species contribute to nitrogen fixation, a crucial process converting atmospheric nitrogen into a usable form for plants. This role impacts agricultural productivity.
2. Biotechnology and Industrial Applications:
- Enzyme production: Many Bacillus species produce enzymes with diverse industrial applications, including in food processing, textile manufacturing, and detergent production. Their ability to produce enzymes efficiently and economically is important.
- Antibiotic production: Some Bacillus species produce antibiotics, although many commercially used antibiotics originate from other bacterial genera. The study of Bacillus-produced antibiotics is still ongoing.
- Biopesticides: Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) is a widely used biopesticide, providing a sustainable alternative to chemical pesticides in agriculture. Its application reduces environmental impact.
3. Human Health:
- Pathogens: Some Bacillus species, such as B. anthracis and B. cereus, are human pathogens causing serious diseases. Understanding their pathogenicity mechanisms is critical for developing effective treatments and prevention strategies.
- Probiotics: Certain Bacillus species are being explored for their potential probiotic properties, promoting gut health and immune function. Research in this area is expanding.
Conclusion: A Multifaceted Microorganism
Rod-shaped bacteria, specifically those belonging to the Bacillus genus, represent a remarkably diverse group of microorganisms with significant impacts on various aspects of our lives. From their roles in environmental processes to their applications in biotechnology and their potential as pathogens, understanding their morphology, genetics, and ecological roles is vital. Continuous research and technological advancements are essential in furthering our understanding of this fascinating group of bacteria, leading to advancements in various fields, from medicine and agriculture to environmental science and biotechnology. The multifaceted nature of bacilli highlights the importance of continued investigation into these ubiquitous and influential microorganisms.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is A Webcam An Input Or Output Device
Mar 17, 2025
-
Word For A Person Who Uses Big Words
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Is 375 As A Percentage
Mar 17, 2025
-
Which Is The Correct Order Of The Scientific Method
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Long Is A Thousand Days
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about A Rod Shaped Bacterium Is Called A . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
