4 Protons 5 Neutrons 4 Electrons
News Leon
Mar 19, 2025 · 7 min read
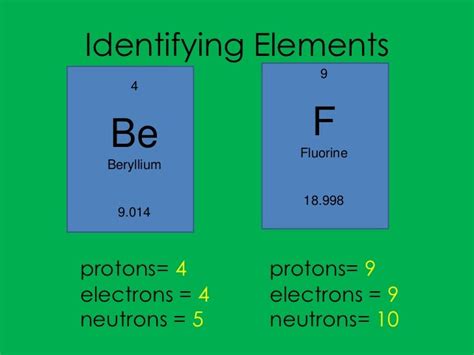
Table of Contents
4 Protons, 5 Neutrons, 4 Electrons: Unveiling the Mystery of Beryllium-9 and its Implications
The seemingly simple combination of 4 protons, 5 neutrons, and 4 electrons might not sound particularly exciting at first glance. However, this specific arrangement of subatomic particles defines the isotope beryllium-9 (⁹Be), an element with a surprisingly rich history, fascinating properties, and significant applications across various scientific disciplines. This article delves into the intricacies of ⁹Be, exploring its nuclear structure, unique characteristics, production methods, applications, and potential future roles in advanced technologies.
Understanding the Fundamentals: Atomic Structure and Isotopes
Before diving into the specifics of ⁹Be, it's crucial to establish a fundamental understanding of atomic structure and isotopes. An atom consists of a nucleus containing protons and neutrons, surrounded by orbiting electrons. The number of protons determines the element's atomic number and its position on the periodic table. For beryllium, this number is 4, indicating four protons in its nucleus.
Neutrons, while electrically neutral, contribute significantly to the atom's mass and stability. The total number of protons and neutrons is known as the mass number. Isotopes are atoms of the same element (same number of protons) but with varying numbers of neutrons, resulting in different mass numbers. Beryllium has several isotopes, but ⁹Be, with 5 neutrons and a mass number of 9, is by far the most abundant and stable isotope found in nature, making up nearly 100% of naturally occurring beryllium.
The presence of 4 electrons in ⁹Be balances the positive charge of the 4 protons, resulting in a neutral atom. These electrons occupy specific energy levels or orbitals, determining the atom's chemical reactivity and its ability to form bonds with other atoms. Understanding these basic concepts provides a solid foundation for comprehending the unique characteristics and behavior of ⁹Be.
The Nuclear Structure of Beryllium-9 (⁹Be)
The arrangement of protons and neutrons within the ⁹Be nucleus is a key determinant of its properties. Unlike many other light nuclei, ⁹Be exhibits an interesting nuclear structure. It's neither particularly stable nor exceptionally unstable. This “intermediate” stability stems from the specific interplay between the strong nuclear force (which binds protons and neutrons together) and the electromagnetic force (which repels protons). The five neutrons in ⁹Be play a crucial role in overcoming the repulsive forces between the four protons, leading to a relatively stable configuration.
The relatively low binding energy per nucleon in ⁹Be compared to neighboring nuclei suggests that it occupies a region of the nuclear landscape where the balance of nuclear forces is delicate. This delicate balance makes ⁹Be susceptible to various nuclear reactions, including neutron absorption, alpha decay, and other nuclear processes, providing avenues for its utilization in nuclear research and applications.
Production and Sources of Beryllium-9
⁹Be isn't readily found in isolation. Its primary source is the extraction from naturally occurring minerals like beryl (Be₃Al₂(SiO₃)₆) and bertrandite (Be₄Si₂O₇(OH)₂). These minerals are mined, and a complex chemical process is employed to separate the beryllium from the other elements present. This extraction process is energy-intensive and requires specialized equipment and expertise due to the toxicity of beryllium compounds and the high reactivity of beryllium metal.
The relatively low abundance of beryllium in the Earth's crust adds to the challenge of production. While not considered a rare element, it’s scattered throughout various minerals, requiring substantial effort and resources for its extraction and purification.
The Unique Properties and Characteristics of Beryllium-9
The unique combination of its atomic structure and low atomic mass gives ⁹Be a distinctive set of properties. Some key characteristics include:
- High strength-to-weight ratio: Beryllium is exceptionally light and strong, making it a valuable material in aerospace and other high-performance applications.
- High thermal conductivity: Beryllium boasts an exceptional ability to conduct heat, crucial for applications where efficient heat dissipation is essential.
- Low density: Its incredibly low density, even lower than aluminum, makes it ideal for applications where weight is a critical factor.
- High modulus of elasticity: Beryllium’s high stiffness ensures excellent dimensional stability, essential in precision instruments and engineering applications.
- Transparency to X-rays: Its transparency to X-rays makes it useful in X-ray windows for scientific instruments and medical applications.
- Neutron reflectivity: ⁹Be's ability to reflect neutrons makes it valuable in nuclear reactor technology and neutron scattering experiments.
Applications of Beryllium-9 Across Diverse Fields
The unique characteristics of ⁹Be translate into numerous applications across various scientific and technological fields:
1. Aerospace and Defense:
- Aircraft and spacecraft components: Beryllium’s lightweight yet high-strength properties make it a preferred material for high-performance aircraft and spacecraft components, where minimizing weight is crucial for fuel efficiency and maneuverability.
- Missile guidance systems: Its dimensional stability and high stiffness are highly valued in the precision manufacturing of missile guidance systems.
- Satellite instruments: Beryllium's high thermal conductivity ensures efficient cooling of delicate satellite instruments exposed to extreme temperature variations in space.
2. Nuclear Technology:
- Neutron reflectors and moderators: Beryllium's ability to reflect and moderate neutrons makes it essential in nuclear reactors for controlling the chain reaction and enhancing efficiency.
- Neutron sources: Certain nuclear reactions involving ⁹Be can produce neutrons, making it useful in applications requiring neutron beams for research and industrial processes.
- Target materials for particle accelerators: Beryllium targets are employed in particle accelerators to generate high-energy particle beams for various research purposes.
3. Medical Applications:
- X-ray windows: Beryllium's transparency to X-rays makes it ideal for manufacturing windows in X-ray tubes and other medical imaging devices.
- Radiation shielding: Though less common than lead, beryllium can be used in specialized applications requiring radiation shielding due to its lighter weight and high strength.
4. Electronics and Optics:
- High-frequency applications: Beryllium’s high thermal conductivity and dimensional stability are advantageous in high-frequency electronic applications.
- Optical mirrors and windows: Its high reflectivity in the ultraviolet region and ability to maintain precise shape makes it useful for high-precision optical mirrors and windows.
5. Other Applications:
- Sporting goods: The lightweight and strong nature of beryllium finds niche applications in high-performance sporting goods, such as golf club heads.
- High-precision instruments: Beryllium’s dimensional stability makes it ideal for constructing components in high-precision instruments requiring minimal distortion.
Future Directions and Research in Beryllium-9
Despite its numerous applications, research into ⁹Be and its applications is constantly evolving. Future research areas include:
- Advanced material science: Researchers are exploring the potential of beryllium-based composites and alloys to enhance its properties and expand its applications in more demanding environments.
- Nuclear fusion: The unique interaction of ⁹Be with neutrons is crucial in ongoing research for nuclear fusion reactors, where beryllium plays a significant role in plasma confinement and neutron production.
- Medical isotopes: Future research aims at exploring the potential use of beryllium-derived isotopes in novel medical therapies and imaging techniques.
- Environmental impact: Research on minimizing the environmental impact of beryllium extraction and processing is crucial for sustainable development.
Toxicity and Safety Considerations
It is crucial to acknowledge the inherent toxicity of beryllium. Beryllium and its compounds can cause serious health problems, including berylliosis, a chronic lung disease. Proper handling, safety precautions, and stringent regulatory compliance are absolutely necessary when working with beryllium or its compounds.
Conclusion: The Significance of Beryllium-9
The apparently simple combination of 4 protons, 5 neutrons, and 4 electrons in ⁹Be gives rise to an element with a remarkable array of properties and applications. From its critical role in high-performance aerospace technology and nuclear reactors to its use in medical imaging and precision instruments, ⁹Be's impact across numerous fields is undeniable. However, its toxicity necessitates careful handling and responsible application. As research progresses, the potential applications of ⁹Be are likely to expand further, shaping advancements in technology and scientific understanding for years to come. Further exploration of its unique nuclear characteristics promises to unlock even greater possibilities and applications in the future.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Is Not A Unit Of Mass
Mar 20, 2025
-
Is Concave Mirror Converging Or Diverging
Mar 20, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Statement Is True About Todays World
Mar 20, 2025
-
Snowfall Doesnt Always Occur In Brazil
Mar 20, 2025
-
Which Continent Is Closest To Antarctica
Mar 20, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 4 Protons 5 Neutrons 4 Electrons . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
